Transformers
Understanding the Latest Advancements in Language Modeling
In the field of natural language processing (NLP), language modelling is a key task that involves predicting the probability of a sequence of words in a given language. In recent years, the development of transformer models has revolutionized the field of NLP, enabling the creation of more powerful and accurate language models than ever before.
A transformer is a type of neural network architecture that was first introduced in a 2017 paper by Vaswani et al. Since then, transformer models have become the state-of-the-art approach for a wide range of NLP tasks, including language translation, text summarization, and question-answering.
The key innovation of the transformer model is its use of self-attention mechanisms, which allow the model to attend to different parts of a sequence of input words when making predictions. This enables the model to capture more complex patterns and relationships between words, leading to more accurate predictions.
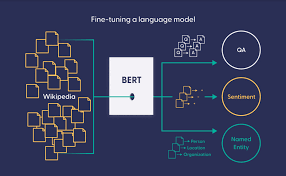
One of the most famous transformer models is BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers), which was introduced by Google in 2018. BERT is a pre-trained language model that is trained on a large corpus of text data, and can then be fine-tuned for specific NLP tasks with relatively small amounts of task-specific data. Since its release, BERT has become a widely-used tool for a wide range of NLP tasks, from sentiment analysis to named entity recognition.
Another popular transformer model is GPT-3 (Generative Pre-trained Transformer 3), which was released by OpenAI in 2020. GPT-3 is an even larger and more powerful language model than BERT, with 175 billion parameters. It has been trained on an enormous corpus of text data, and can generate highly realistic and coherent text in a wide range of styles and formats.
One of the most exciting things about transformer models is their potential to revolutionize the way we interact with language. For example, with the development of more powerful and accurate language models, it may be possible to create more advanced chatbots and conversational agents that can understand and respond to human language more accurately and effectively. Similarly, transformer models could enable the creation of more sophisticated language translation and summarization tools that could be used to bridge language barriers and help people access information in different languages.
However, there are also potential downsides to the development of more powerful language models. For example, there are concerns about the potential for these models to be used to generate fake news or propaganda or to perpetuate harmful biases or stereotypes. As with any new technology, it will be important for researchers, developers, and policymakers to consider the potential ethical implications of these advancements in language modelling.
Transformer models represent a major breakthrough in the field of natural language processing, enabling the creation of more powerful and accurate language models than ever before. As these models continue to evolve, they have the potential to transform the way we interact with language and create new opportunities for communication and collaboration. However, it is important to also consider the potential ethical implications of these advancements and work to ensure that they are developed and deployed responsibly.
We research, curate and publish daily updates from the field of AI.
Consider becoming a paying subscriber to get the latest!
No spam, no sharing to third party. Only you and me.