Future Impacts of Generative AI and its Potential
Generative AI as a Technology Catalyst:
The breakthroughs that have led to the rise of generative AI have been decades in the making. Investments in machine learning and deep learning have paved the way for tools like ChatGPT, GitHub Copilot, and Stable Diffusion, which have gained widespread attention. These investments have enabled the integration of AI applications into everyday products and services, even if their progress has been gradual and often unnoticed.
Unlike previous AI milestones, such as AlphaGo's victory over a Go champion, generative AI tools like ChatGPT have captured the imagination of people worldwide. Their broad utility and ability to engage in conversations with users have made them popular for communication and creativity. While generative AI can perform routine tasks like data organization, it is its capacity to write text, compose music, and create digital art that has made headlines and sparked experimentation among consumers.
The development of foundation models, which are expansive artificial neural networks inspired by the human brain, has been instrumental in the advancement of generative AI. These models, a part of deep learning, enable the processing of large and diverse sets of unstructured data and the performance of multiple tasks. Generative AI based on foundation models has improved existing capabilities and introduced new ones across various modalities such as images, video, audio, and computer code.
However, continued innovation in generative AI also brings challenges. Training generative AI with hundreds of billions of parameters requires significant computational power, which could become a bottleneck in development. Efforts to make AI more responsible, driven by the open-source community and AI companies themselves, may also increase its costs.
Despite these challenges, funding for generative AI is significant and growing rapidly. In the first five months of 2023 alone, investments in generative AI reached $12 billion. Venture capital and private investments in generative AI have seen an average compound growth rate of 74 percent annually from 2017 to 2022, outpacing the growth rate of overall AI investments.
Generative AI capabilities have developed rapidly, as evidenced by the progress of tools like ChatGPT, GPT-4, and Claude. Companies like Google have also announced new features powered by generative AI. The majority of external private investment in generative AI is concentrated in North America, reflecting the dominance of the region in the AI investment landscape.
Generative AI has the potential to reshape knowledge work across industries and business functions, from sales and marketing to customer operations and software development. Its transformative capabilities can unlock trillions of dollars in value across sectors like banking and life sciences. This report examines the value generative AI can create for companies and the resulting impact on the workforce, providing insights into its potential.
Key Insights on the Economic Potential of Generative AI:
- Enormous economic impact: Generative AI has the potential to add $2.6 trillion to $4.4 trillion annually to the global economy, surpassing the GDP of many countries. This represents a 15 to 40 percent increase in the overall impact of artificial intelligence. When considering the integration of generative AI into existing software, the estimate could double.
- High-value areas: Approximately 75 percent of the value generated by generative AI lies within customer operations, marketing and sales, software engineering, and R&D. Across various business functions, there are 63 use cases where generative AI can provide measurable outcomes. Examples include enhancing customer interactions, creating creative marketing content, and automating code generation.
- Industry-wide impact: Generative AI will significantly impact all industry sectors. Sectors such as banking, high tech, and life sciences are expected to experience substantial revenue gains from generative AI. For instance, the banking industry could see an additional value of $200 billion to $340 billion annually, while retail and consumer packaged goods could benefit by $400 billion to $660 billion per year.
- Transformation of work: Generative AI has the potential to change how work is done by automating a large portion of individual work activities. With the ability to automate 60 to 70 percent of current employee tasks, generative AI surpasses previous estimates of technology automation. Its impact is particularly significant in knowledge-based work that demands higher wages and educational qualifications.
- Accelerated workforce transformation: The potential for technical automation, including generative AI, is expected to expedite workforce transformation. Revised scenarios indicate that between 2030 and 2060, around 50 percent of work activities could be automated, with a midpoint of 2045—roughly a decade earlier than previous estimates.
- Increased labor productivity: Generative AI has the capacity to substantially enhance labor productivity. By supporting workers in shifting activities or transitioning to new jobs, generative AI could contribute to annual labor productivity growth of 0.1 to 0.6 percent until 2040. When combined with other technologies, work automation could add 0.2 to 3.3 percentage points to annual productivity growth. However, it is crucial to invest in worker support and skill development to maximize these gains.
- Early stage of development: While generative AI holds great promise, its full potential will take time to realize. Leaders in business and society face challenges in managing the risks associated with generative AI, determining the workforce's required skills and capabilities, and rethinking core business processes to accommodate retraining and skill development. Despite these challenges, the excitement surrounding generative AI's early pilots indicates a promising future.
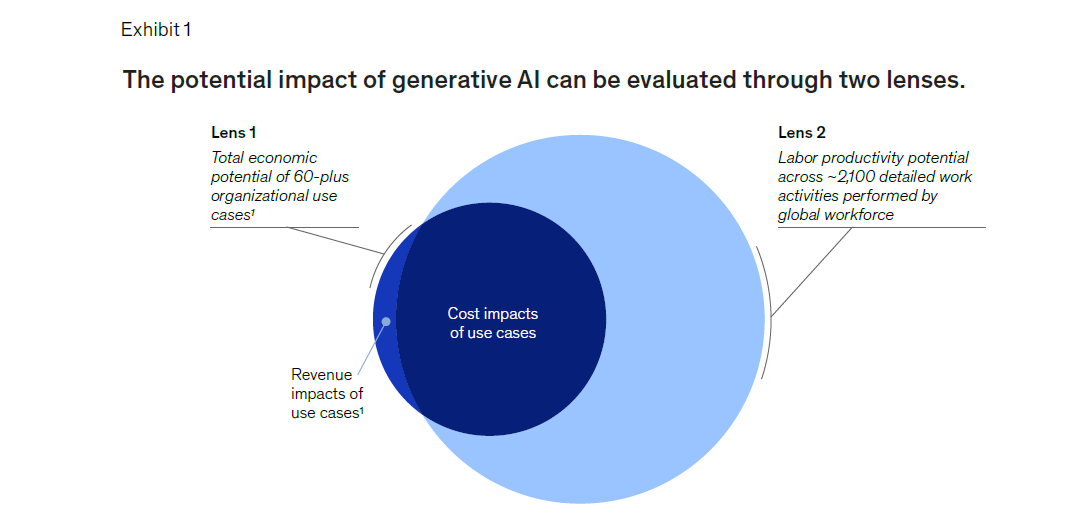
McKinsey has identified 63 use cases across 16 business functions. These use cases have the potential to generate economic benefits ranging from $2.6 trillion to $4.4 trillion annually when implemented across industries. This substantial value addition, which amounts to 15 to 40 percent of the economic value unlocked by non-generative AI and analytics, signifies the significant role generative AI can play in driving economic growth.
Additionally, McKinsey has analyzed the impact of generative AI on labor productivity by estimating its potential to perform over 2,100 detailed work activities across 850 occupations. With generative AI's current capabilities, it is expected to enhance labor productivity and result in economic benefits totaling $6.1 trillion to $7.9 trillion annually. This estimation considers the overlap with cost reductions in the use cases analysis, focusing on the value generated by applying generative AI to the activities of knowledge workers worldwide.
While generative AI is an evolving and exciting technology, it is essential to recognize that other applications of AI still account for the majority of its overall potential value. Traditional advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms excel in numerical and optimization tasks, finding applications across various industries. However, generative AI, with its creative and innovative capabilities, pushes the boundaries of what AI can achieve, expanding possibilities and offering new opportunities.
To estimate the value potential of generative AI use cases, McKinsey utilized a proprietary database and consulted over 100 industry experts. Their analysis focused on use cases where generative AI techniques, primarily transformer-based neural networks, can address challenges not well tackled by previous technologies. The estimated value potential does not include use cases solely relying on natural language processing but considers the significant improvements generative AI can bring to key value-driving outputs.
In terms of business function, generative AI exhibits the highest impact relative to functional cost in customer operations, marketing and sales, software engineering, and research and development. These four functions alone account for approximately 75 per cent of the total annual value derived from generative AI use cases. Notably, the potential value of generative AI in manufacturing and supply chain functions, which were prominent in previous AI use case analyses, is now relatively lower due to the nature of generative AI use cases focusing on creative and non-numerical applications.
Beyond function-specific use cases, generative AI holds the potential to revolutionize internal knowledge management systems within organizations. With its remarkable natural-language processing capabilities, generative AI can serve as a virtual expert, enabling employees to retrieve stored knowledge through human-like queries and engaging in an ongoing dialogue. This empowers teams to access relevant information swiftly, facilitating informed decision-making and strategy development. By relieving knowledge workers of time-consuming information search tasks, generative AI can significantly improve efficiency and effectiveness in organizations.
Generative AI presents substantial economic potential across a wide range of use cases and business functions. Its impact on labour productivity and the ability to act as a virtual expert offer transformative possibilities for industries and organizations. As generative AI continues to advance, it has the potential to reshape the business landscape and unlock new avenues for growth and innovation.
Reference: McKinsey & Company-The economic potential of generative AI: The next productivity frontier
We research, curate and publish daily updates from the field of AI. Paid subscription gives you access to paid articles, a platform to build your own generative AI tools, invitations to closed events and open-source tools.
Consider becoming a paying subscriber to get the latest!
No spam, no sharing to third party. Only you and me.